Proteins
Introduction
Did you know water is the most abundant molecule in fat free bodily tisses, and protein is the 2nd most abundant? Proteins main roles include acid–base balance, energy production, cell signaling, and nutrient transport…
Protein Structure
So their are inorganic and organic molecules…Organic molecules contain carbon, Inorganic do not. Hence why organic chemistry is a whole series of chemistry on Carbon. Inorganic molecules include see pic below.
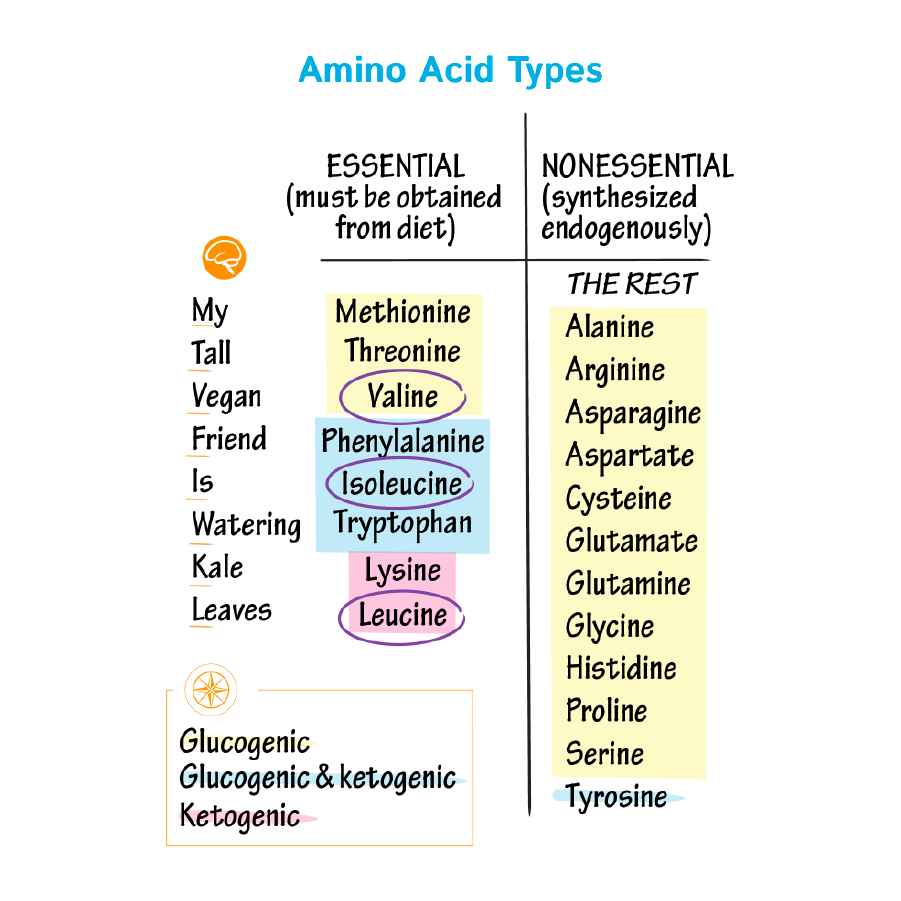
Protein is made from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; protein is different from carbohydrate and fats in that it also has nitrogen. I’m sure you’ve heard of the word amino acid. For a protein to be “complete” it needs all 9 of the essential amino acids, which I covered in this post here. Amino acids make up the protein, and the elements nitrogen (N), carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) huddle together and form the “LEGOS” of protein, aka amino acids.
Amino Acids
The structure and formation of amino acids include 5 dimensions:
Central carbon
Carboxyl group (organic acid – COOH)
Hydrogen
Amino group (NH2)
Side chain (R group)
You’ve probably heard of the debate between animal protein vs vegetarian protein, and it often comes down to which source has the essential amino acids (EAA) we need; they are necessary for bodily functions and cannot be synthesized or “bundled” in the body:
There are 9 EAAs, which include three branched chain amino acids
There are 6 conditionally EAA
Unlike EAAs, they can be synthesized in the body. The conditionally EAA may be essential for some individuals, and thus must be obtained in the diet; however for a typical healthy adult the main goal is to consume protein with the 9 EAA. The conditionally EAA become essential during infancy, injury, disease, or trauma.
You’ll notice some of these amino acids are classified into 3 categories:
Glucogenic
Glucogenic & Ketogenic
Ketogenic
What this means is the potential for the amino acids to become glucose or ketones. During times of a negative balance in the system, the body will turn to the glucose or ketones to rely on for energy production.
Gluconeogenesis: the process by which the Glucogenic amino acids have their carbon backbone converted to glucose (turning a protein into glucose)
The Krebs cycle is a series of chemical reactions with the intent to produce energy
Protein and Digestion
So we have a organ called the liver, and one of its jobs with the amino acids may be used for protein synthesis. According to this study, about 85% of plant protein and 95% of animal protein is absorbed.
Hormones and Neurotransmitters
Did you know hormones are derived from amino acids? Also known as peptide hormones. Human growth hormone, made by pituitary gland, for example have 191 amino acids…maybe the reasoning behind youthful aging is a high protein diet and exercise as research continues to suggest……..Other peptide hormones include insulin gastrin made in stomach, and leptin, made in fat tissue.
Peptide hormones may also act as neurotransmitters. They both have similar roles in that they both serve as chemical messengers:
Neurotransmitters are part of the nervous system
Hormones are part of the endocrine system
For example:
Oxytocin, a peptide hormone and neurotransmitter
Hormone: signals the release of breast milk after giving birth
Neurotransmitter: stimulates feelings of social connection and sexual attraction
Other peptides that are also acting as neurotransmitters: epinephrine, glutamate, dopamine, serotonin, and histamine
How much protein should I take?
Weight training crowd: 1.8 -2.2 grams of protein/kg of bodyweight
Cardio crowd: 1.2-1.7 grams of protein/kg of bodyweight
Mr. Special Leucine
Amino acid leucine is associated with muscle recovery and growth aka known to reliably enhance muscle anabolism. You still need all 9 EAA though. However, it is important to understand that leucine is operating as a signal and all of the amino acids are still necessary to form proteins. If the goal is to optimize muscle growth during the “post workout” window, it’s best after 3 hrs of working out to consume leucine high food. According to this study,: Leu content of dietary proteins is important for muscle protein synthesis and highlights the need for long-term studies examining the impact of Leu density on muscle health and body composition.
Carbohydrates
Introduction
Put simply their are complex or simple carbohydrates; starches or sugars. Complex carbs usually have fiber, and simple do not. Starches are grains, vegetables, rice, barley. Sugars are lactose, fruits, fructose, cane sugar, candy.
Examples of added sugars:
White, brown, and raw sugar
Agave, honey
Date sugar
Molasses
Caramel
Maple sugar or syrup
Corn sweetener or syrup
Turbinado sugar
Rice syrup etc.
Fiber
Fiber is one of the main components to weight loss, aside from protein; they’re generally classified as soluble or insoluble
Soluble fiber is dissolved when placed in water, and can be found in oat bran, oatmeal, beans, fruits, and vegetables and may benefit for:
Weight loss: promote a feeling of full
Reducing risk for cardiovascular disease: It can bind to cholesterol particles, and remove them from body
Defend against constipation, Bowel movement and intestinal health: soluable fiber loves water so it can help bulk up the stool
Protect against diabetes, limiting spikes in blood sugar
Slow movement of foods in intestine and promote nutrient absorption
Insoluble fiber has similar benefits, but can be found in different foods.
How Carbohydrates Operate in the Body…Digestion/Absorption
Digestion begins in the mouth via the enzyme amylase released by the salivary glands. Their is a reason why you were told to eat slow, and chew your food. The chewing chewing breaks the food into smaller pieces called bolus, and the grinding of the food may help facilitate digestion and absorption. I once heard you want to chew about 20 seconds per bite. Once the carbs are digested into monosaccharides, it enters the bloodstream and into the liver then will replenish depleted glycogen in the cells and/or store as fat.
Glucose, Glucagon, and Insulin
Both hormones insulin and glucagon work to preserve blood glucose. Insulin is released from the pancreas with it’s job of lowering blood sugar levels by calling on the glucose in the blood and push it into the liver, muscle, and fat.
Glucagon is also released from the pancreas and works to raise blood sugar levels when low. Glucagon is the hormone responsible for telling the liver to release glucose into the bloodstream.
Insulin production from the pancreas is highly reliant on the state of the beta cells in the pancreas. If some people, the beta cells may stop producing insulin…can call it beta cell insufficiency. This is typically genetic, and is called type1 diabetes where one would need to rely on exogenous insulin since their body is not producing enough. Type 2 diabetes is not genetic like type 1, and is due to lack of cell sensitivity to insulin thus causing the sugar in the bloodstream to stay in the bloodstream and not go into the cells. Type 2 can be reversed through proper weight loss and diet. Adopting an exercise regimen with weight training, keto dieting, intermittent fasting as well as using a supplement called dihydroberberine are all useful to facilitate weight loss and improve cell sensitivity.
Fats
Introduction
Saving the best macronutrient for last….fats! It’s the main macronutrient with a high density amount of calories. For 1 gram of fat you get 9 calories. Fat is responsible for metabolizing fat soluble vitamines: A, D, E, and K.
Fat is one of the three macronutrients of the human diet. Dietary fat is important for our survival and has many important functions in our bodies, such as being a major source of energy, metabolizing fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), and obtaining essential fatty acids. Unlike protein and carbohydrates, fat is hydrophobic and is not soluble in water. In other words, water and oil do not mix, no matter how much you shake or stir these two substances.
Saturated vs Unsaturated
Unsaturated fatty are also known as monounsaturated or polyunsaturated. The difference between the saturated and unsaturated is the saturated has a single chemical bond between the carbon atoms; whereas the unsaturated has a double bond between the carbon atoms.
Unsaturated fatty acids normally last longer and not prone to oxidative stress; Saturated fatty acids are more quick to expire , hence why you’ll notice your avocados start to go bad after some time of storing them away.
Monounsaturated fats include olive oil, almonds, cashews, canola oil, avocados etc. You’ll find the mediterranean diet has a lot of monounsaturated fats. Including more monounsaturated fats may be helpful for a healthy heart. Polyunsaturated fats include salmon, walnuts, sunflower seeds, flax oil etc. it’s wise to choose monounsat and polyunsat fats over saturated fats and transfats.
Trans Fats
Trans fat, literally nothing good about them. If you read the nutrition label of butters such as JIF Peanut Butter, you’ll notice it states hydrogenated vegetable oil. Too much can imply the product has transfats, but the food companies technically aren’t required to put it on the label that it has transfats because the nutrition labels are suggesting the estimated calorie amount per serving* which may suggest that consuming more than the serving size, that it has transfats. Hydrogenation is a processing mechanism that puts hydrogen into the food to make it saturated so it lasts longer. Other foods with hydrogenation in is are basically all things you hear not to eat: doughnuts, fried foods, french fries, fried chicken, etc.
Good Fats, Essential Fatty Acids
You probably already know to eat your Omega 3 and Omega 6 fatty acids…Their is also another component that is found in plant oils such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, flaxseed oil and that’s alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). You probably have read it on the nutrition label. Then their is eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) omega-3 fatty acids which are found in cold-water fatty fish: salmon, mackerel, and crab. It’s useful to note and you know that eating more salmon because it’s high in EPA and DHA may help with decreasing heart events. It’s pushed in the articles about nutrition and people are told to eat more of it yet people don’t seem to listen and continue to eat crap… You are what you eat, eat well and your body will take care of you. One of the reasons EPA and DHA sources like salmon are so good is because of its anti-inflammatory properties and brain development with a ton of other benefits. Another fatty acid our bodies don’t naturally produce is omega 6 also called linoleic acids which can be found in nuts and seeds. Don’t fall prey to processed foods claiming to have omega 6 in it…..it should come from a natural source. So, eat your almonds.
Conclusion
Well that’s all for now. Now you have every good reasons to start eating well for health and longevity.
Subscribe to the other stuff and click below for more.